publications
2026
-
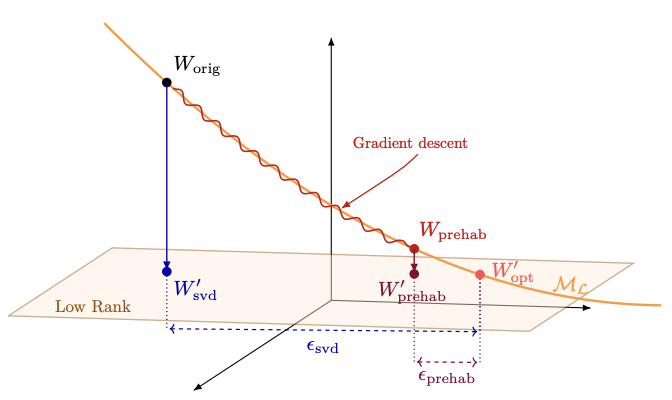 Low-Rank Prehab: Preparing Neural Networks for SVD CompressionHaoran Qin, Shansita Sharma, Ali Abbasi, and 2 more authors2026
Low-Rank Prehab: Preparing Neural Networks for SVD CompressionHaoran Qin, Shansita Sharma, Ali Abbasi, and 2 more authors2026Low-rank approximation methods such as singular value decomposition (SVD) and its variants (e.g., Fisher-weighted SVD, Activation SVD) have recently emerged as effective tools for neural network compression. In this setting, decomposition acts as a "surgical" intervention, followed by fine-tuning that serves as "rehab" to recover accuracy. Inspired by prehabilitation in surgery, we introduce a pre-compression fine-tuning stage, Low-Rank Prehab, that explicitly encourages low-rank structure in weight matrices while preserving task performance. By conditioning the model before SVD, Prehab steers weights toward spectrally compact regions of the parameter space, enabling smoother low-rank approximation and improved recovery. Experiments on large language models (LLMs) and other Transformer-based architectures, including Vision Transformers (ViTs), show that Prehab substantially reduces the immediate accuracy drop after compression and consistently improves post-finetuning performance. Across a wide range of compression ratios, our method outperforms state-of-the-art SVD-based techniques such as SVD-LLM, highlighting the importance of preparing models for compression rather than only improving the compression and recovery stages.
-
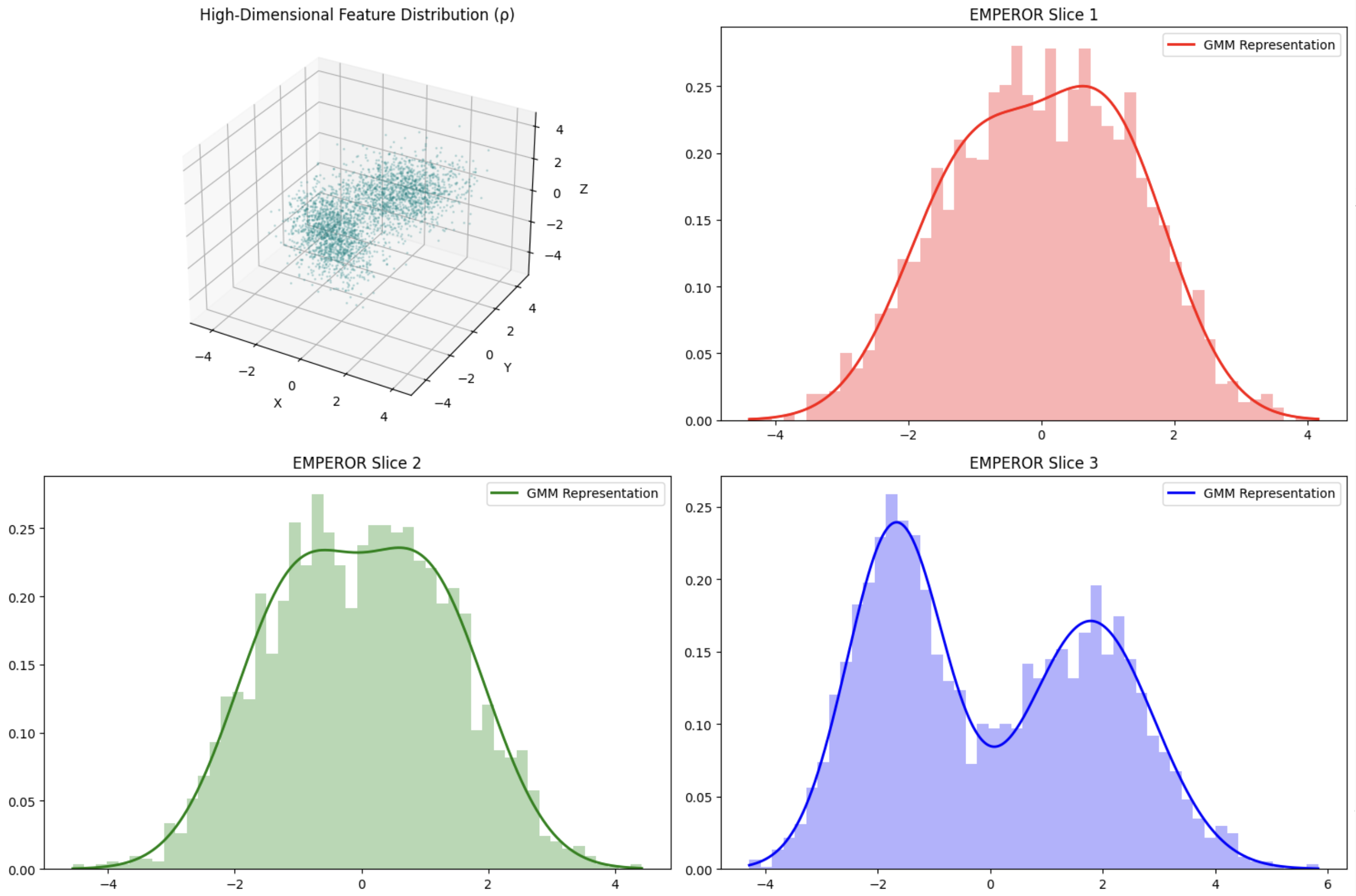 EMPEROR: Efficient Moment-Preserving Representation of DistributionsXinran Liu, Shansita D. Sharma, and Soheil Kolouri2026
EMPEROR: Efficient Moment-Preserving Representation of DistributionsXinran Liu, Shansita D. Sharma, and Soheil Kolouri2026We introduce EMPEROR (Efficient Moment-Preserving Representation of Distributions), a mathematically rigorous and computationally efficient framework for representing high-dimensional probability measures arising in neural network representations. Unlike heuristic global pooling operations, EMPEROR encodes a feature distribution through its statistical moments. Our approach leverages the theory of sliced moments: features are projected onto multiple directions, lightweight univariate Gaussian mixture models (GMMs) are fit to each projection, and the resulting slice parameters are aggregated into a compact descriptor. We establish determinacy guarantees via Carleman’s condition and the Cramér-Wold theorem, ensuring that the GMM is uniquely determined by its sliced moments, and we derive finite-sample error bounds that scale optimally with the number of slices and samples. Empirically, EMPEROR captures richer distributional information than common pooling schemes across various data modalities, while remaining computationally efficient and broadly applicable.
-
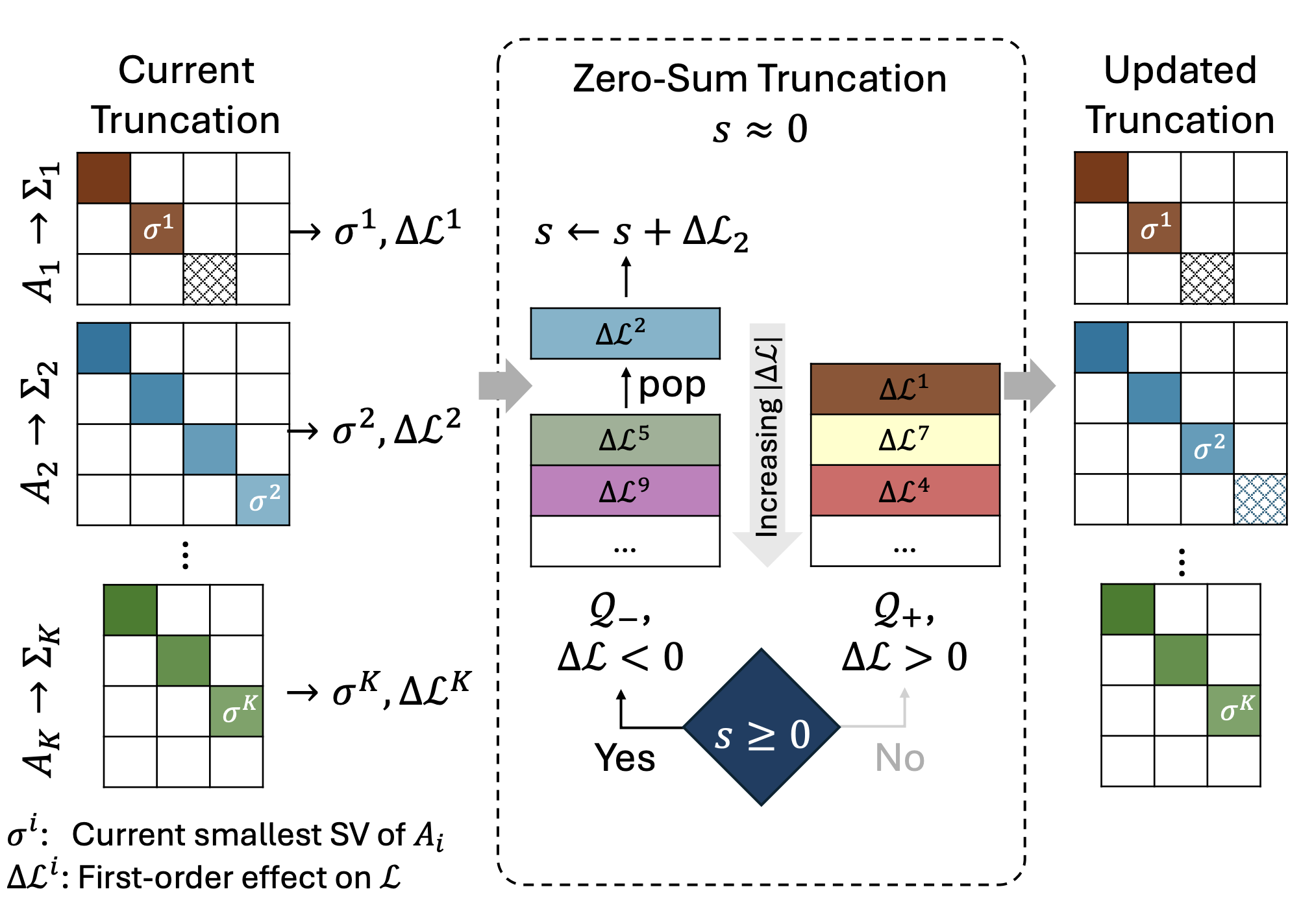 Zero Sum SVD: Balancing Loss Sensitivity for Low Rank LLM CompressionAli Abbasi, Chayne Thrash, Haoran Qin, and 3 more authors2026
Zero Sum SVD: Balancing Loss Sensitivity for Low Rank LLM CompressionAli Abbasi, Chayne Thrash, Haoran Qin, and 3 more authors2026Advances in large language models have driven strong performance across many tasks, but their memory and compute costs still hinder deployment. SVD-based compression reduces storage and can speed up inference via low-rank factors, yet performance depends on how rank is allocated under a global compression ratio. Prior methods often use homogeneous ranks for similarly sized matrices, despite large differences in loss sensitivity, or rely on expensive iterative pre-truncation optimization to determine per matrix ranks. We propose \textbfZero Sum SVD (\textbfZS-SVD), a post-training method that performs \emphglobal singular component selection using activation whitening and first-order calibration loss estimates in whitened coordinates. \textbfZS-SVD prunes components across the whole model with a \textbfzero sum rule that keeps the cumulative predicted loss change near zero, automatically yielding heterogeneous ranks without solving a rank allocation optimization. Motivated by evidence that gradients near pretrained solutions exhibit low rank structure, we also introduce an optional lightweight correction that applies a \textbfsingle projected gradient update after truncation, followed by re-truncation. Extensive experiments across multiple LLM architectures show consistent gains across diverse benchmarks and compression ratios.
2025
-
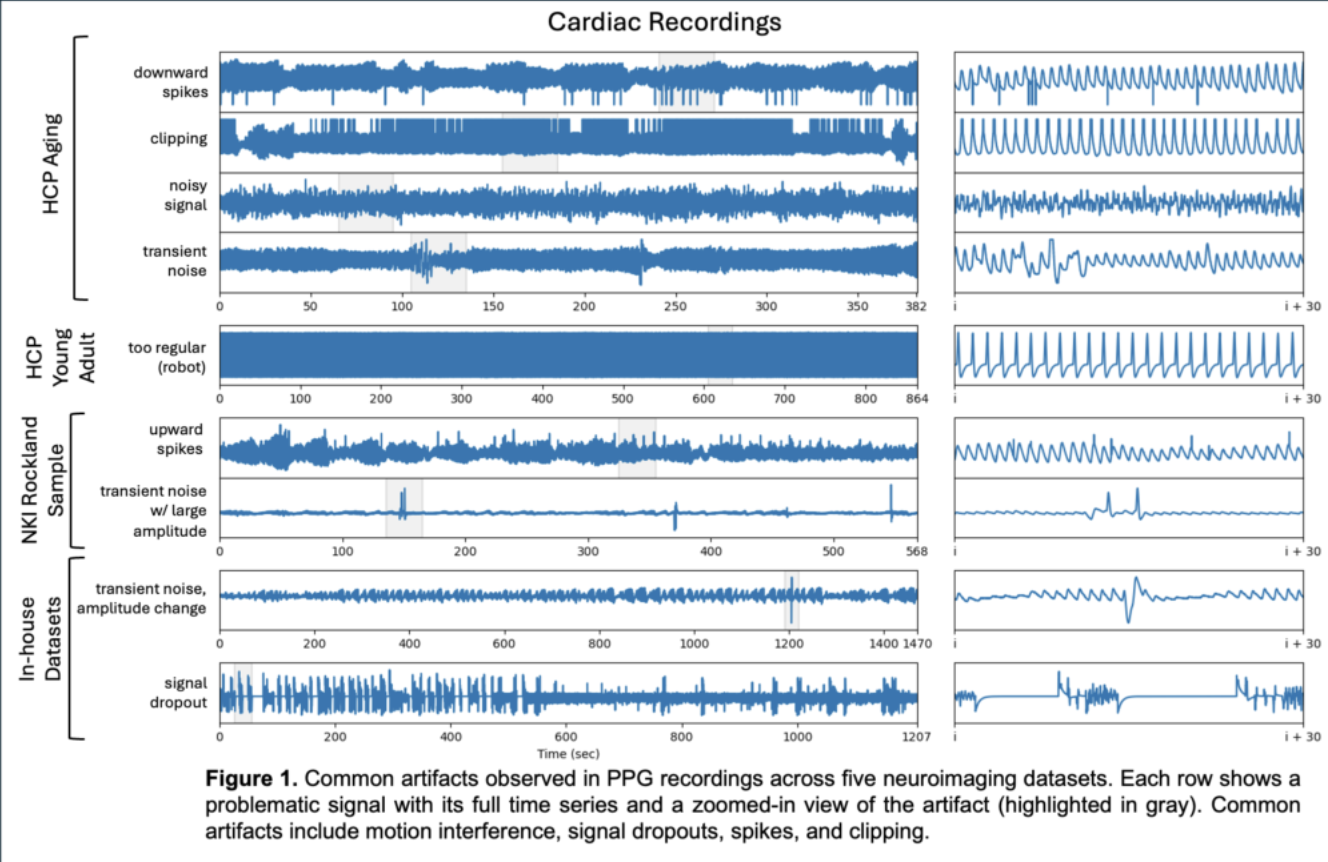 A Collaborative Framework for Standardizing Physiological Data Quality Assessment in NeuroimagingRithwik Guntaka, Shansita Sharma, Richard Song, and 8 more authors31st Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping (OHBM), 2025
A Collaborative Framework for Standardizing Physiological Data Quality Assessment in NeuroimagingRithwik Guntaka, Shansita Sharma, Richard Song, and 8 more authors31st Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping (OHBM), 2025This paper presents a collaborative framework for standardizing the assessment of physiological data quality in neuroimaging studies. The framework aims to address the challenges posed by the diverse and often inconsistent quality of physiological data collected across different neuroimaging modalities and studies. By establishing a set of common criteria and best practices for data quality assessment and the framework seeks to enhance the reproducibility and comparability of neuroimaging research findings. The paper discusses the key components of the framework and including data acquisition and preprocessing and and quality evaluation and and highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing the field of neuroimaging.
2024
-
 Comparison of Transfer Learning Techniques for Building Energy ForecastingShansita Das Sharma, Austin Coursey, Marcos Quinones-Grueiro, and 1 more authorIFAC Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety for Technical Processes (SAFEPROCESS), 2024
Comparison of Transfer Learning Techniques for Building Energy ForecastingShansita Das Sharma, Austin Coursey, Marcos Quinones-Grueiro, and 1 more authorIFAC Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety for Technical Processes (SAFEPROCESS), 2024The growing demand for building energy efficiency necessitates accurate predictions of normal versus abnormal operations to understand their impact on energy management. However, integrating predictive models into practical applications faces challenges, especially in buildings with limited measurements and data. This paper explores the viability of three widely adopted transfer learning techniques in improving energy consumption models, focusing on real-world data with internal building measurements. The findings suggest that transferring information between buildings is a promising method to provide positive improvements in energy prediction models.